New to crypto and want an introduction? You’ve come to the right place!

Cryptocurrencies have been attracting a lot of interest lately. You can regularly find them being mentioned on the news, from a relative, or on Netflix. Decryptionary is a dictionary covering the subject of cryptocurrency and its technology. I created Decryptionary as a point of entry for those who know very little about the subject.
Let’s start with the key terms:
What is cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is an electronic money created with technology controlling its creation and protecting transactions, while hiding the identities of its users.
Crypto- is short for “cryptography”, and cryptography is computer technology used for security, hiding information, identities and more. Currency simply means “money currently in use”.
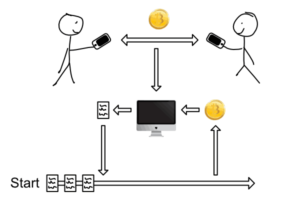
Cryptocurrencies are a digital cash designed to be quicker, cheaper and more reliable than our regular government issued money. Instead of trusting a government to create your money and banks to store, send and receive it, users transact directly with each other and store their money themselves. Because people can send money directly without a middleman, transactions are usually very affordable and fast.
To prevent fraud and manipulation, every user of a cryptocurrency can simultaneously record and verify their own transactions and the transactions of everyone else. The digital transaction recordings are known as a “ledger” and this ledger is publicly available to anyone. With this public ledger, transactions become efficient, permanent, secure and transparent.
With public records, cryptocurrencies don’t require you trust a bank to hold your money. They don’t require you trust the person you are doing business with to actually pay you. Instead, you can actually see the money being sent, received, verified, and recorded by thousands of people. This system requires no trust. This unique positive quality is known as “trustless”.
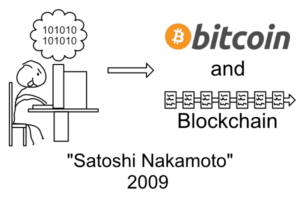
The first cryptocurrency was bitcoin.
What is bitcoin?
Bitcoin is the first digital cash created in 2009. It was made by an unknown person or group who went by the name, Satoshi Nakamoto.
Bitcoin is unique because it does not rely on government/bank created money. In addition, transactions occur directly between pseudonymous people (their real names are not known), meaning there are no banks or middlemen.
Each transaction is recorded on a digital record kept by many people across the world known as the “blockchain”. The data on the blockchain is publicly available and stored on many computers. Because there are so many copies being simultaneously maintained, the transaction and banking data is very safe and virtually impossible to manipulate.
Individuals protect their bitcoins using their digital wallet. A wallet is software that can only be accessed by using a key, which is a long string of letters and numbers.
Bitcoin’s price has risen into the thousands of dollars, but you can still own bitcoin by purchasing a fraction of it for dollars.
What is blockchain?
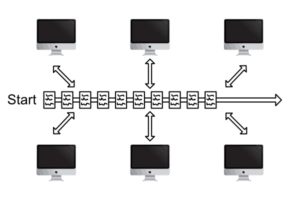
Blockchain is technology for creating permanent, secure digital recordings that don’t rely on any single person or group. Blockchains can record any information, though the first example was created to record bitcoin transactions.
Imagine the blockchain as a book of records. Each page in that book, is a block, and can record anything. Blocks are created one after the other, chained to each other creating what we know as the blockchain.
Multiple blockchain records are maintained simultaneously by many of unrelated individuals and their computers, making it cloud storage on steroids. Updates are seen immediately and manipulation is extremely difficult/impossible. This positive quality known of many people keeping their own copies of the blockchain is known as “distributed”.
There are hundreds of blockchains created by many groups to records all sorts of information including art, medical records, computer information and much more.
But if a blockchain is not distributed among many individuals and instead run by one government, organization, group or person, than it is not at a blockchain at all. A centralized system like that is simply a database.
What is a smart contract?
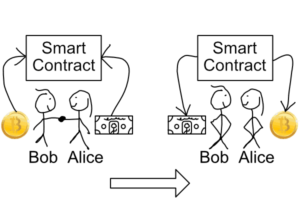
A smart contract mixes blockchain technology with contracts to make a more efficient and affordable system of doing business.
In a smart contract, two people doing business agree to exchange money for something else. if the requirements set by both parties of the contract are met on a date, it activates, delivering what was purchased. If the requirements are not met, the contract deactivates and returns whatever it was storing.
For example, Alice wants 1 bitcoin from Bob and Bob wants $5,000. Both Bob and Alice agree that on January 1, 2018, both the bitcoin and cash will be deposited to the accounts linked with the smart contract.
On January 1st, the contract looks to see if both people fulfilled their obligations. If so, it will release the payment and bitcoin to their new owners. If not, the bitcoin and money are returned to their original owners.
Because the contract is publicly available and unalterable, it is very easy to keep both Bob and Alice responsible for their end of the deal. If anyone somehow violates the agreement, the proof of what they should have done is easily obtained.
What is mining?
Mining is the computer process of recording and verifying information on the digital record known as the blockchain. Because mining requires computer power, people do this work in return for money. Each computer that fulfills this process can earn a reward in digital money and sometimes brand new, virgin coins.
To keep the blockchain network running smoothly, only one block can be created at a time. There are several different ways to do this:
- The most common is known as proof of work and it required computers work hard at solving a math problem. The first computer to solve this problem would discover a new block and could record information on the blockchain. This earned them a reward in brand new digital money plus fees paid for each transaction.
- The next mining technique was called proof of stake. With this system, people who represent a large ownership of coins are selected by the software to create new blocks. Competing people are selected on a lottery-system based on chance. With proof of stake, no new coins are created. Instead fees for verifying and recording transactions are collected.
With over 1,000 cryptocurrencies and many more being created each month, new ways of mining are being explored and discovered.